キネマティックキャラクターコントローラー(KCC)
Introduction
キネマティックキャラクターコントローラー(略してKCC)は、独自のルールセットに従ってキャラクターをワールド内で移動するために使用するものです。KCCを使用すると、物理/力ベースの動きよりも厳密な制御と迅速な動きが可能になります。これらはどのようなゲームでもコアコンセプトではありますが、全体的なゲームプレイに関連しているため、定義は大きく異なります。したがって、Quantum KCCは出発点と見なされます。ただし、開発者はそれぞれの環境で最良の結果を得るために、独自に作成する必要があります。
Quantumには、2D(横スクロール)用と3D移動用の2つのビルド済みKCCが付属しています。 APIを使用すると、キャラクターは地形を移動したり、階段を上ったり、坂を下ったり、移動プラットフォームを使用することができます。
KCCは、動きベクトルを計算するときに、静的オブジェクトと動的オブジェクトの両方の物理データを考慮します。 オブジェクトはキャラクターの動きをブロックし、定義します。 環境オブジェクトとの衝突コールバックもトリガーされます。
必要条件
KKCを使用するかエンティティに追加するには、エンティティにTransformコンポーネントがすでに存在している必要があります。PhysicsBody は使用できますが、必要はありません。物理システムの影響で意図しない動きが発生する可能性があるため、KCCでPhysicsBodyを使用することはお勧めできません。
Quantumの物理に慣れていない場合は、最初に物理エンジンのドキュメントを確認してください。
レイキャストとShapeOverlap
KCCは動きを計算するためにShapeOverlaps(2Dの場合は円、3Dの場合は球)のみを使用します。そのため、KKCコンポーネントのみを持つエンティティは、レイキャストに無視されます。
エンティティがレイキャスティングの対象となる場合は、PhysicsCollider も必要です。
注意
このページでは、2Dおよび3D KCCの両方について説明します。
キャラクターコントローラーコンポーネント
次のいずれかの方法で、CharacterControllerコンポーネントをエンティティに追加できます。
- Unityのエンティティプロトタイプに「Character Controller」コンポーネントを追加する
- コードを介して「Character Controller」コンポーネントを追加する。
コードを介してキャラクターコントローラーを追加するには、以下の例に従ってください。
C#
// 2D KCC
var kccConfig = FindAsset<CharacterController2DConfig>(KCC_CONFIG_PATH);
var kcc = new CharacterController2D();
kcc.Init(f, kccConfig)
f.Add(entity, kcc);
// 3D KCC
var kccConfig = FindAsset<CharacterController3DConfig>(KCC_CONFIG_PATH);
var kcc = new CharacterController3D();
kcc.Init(f, kccConfig)
f.Add(entity, kcc);
注意
コンポーネントは作成後に初期化する必要があります。 使用可能な初期化オプションは次のとおりです。
- (コード)パラメーターなし の
Init()メソッド。Assets/Resources/DB/ConfigsからDefaultCharacterControllerを読み込みます。 - (コード)パラメーターなし の
Init()メソッド。 渡されたCharacterControllerConfigを読み込みます。 - (エディター)
CharacterControllerコンポーネントのConfigスロットにCharacterControllerConfigを追加します。
キャラクターコントローラー設定
Create your own KCC config asset via the context menu under Create > Quantum > Assets > Physics > CharacterController2D/3D.
デフォルトの構成アセット
デフォルトの2Dおよび3D KCC Configアセットは、Assets/Resources/DB/Configsフォルダー内にあります。 3D KCC構成は次のようになります。
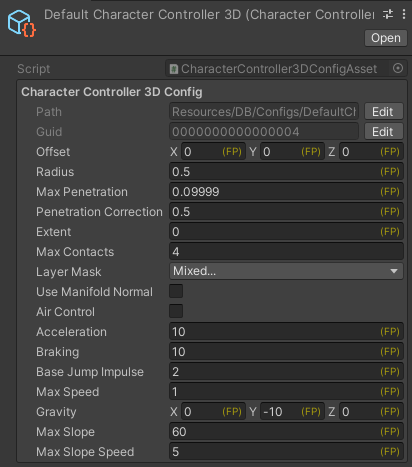
構成フィールドの簡単な説明
- Offset は、エンティティの位置に基づいてKCCローカル位置を定義するために使用されます。これは一般的に、KCCの中心をキャラクターの足に配置するために使用されます。注意:KCCはキャラクターを「移動」するために使用されるため、必ずしもキャラクターの全身を含む必要はありません。
- Radius は文字の境界を定義し、文字の水平サイズを包含する必要があります。キャラクターが特定の方向に移動できるかどうか、壁が動きを妨げているかどうか、階段を上る必要があるかどうか、またはスライドする斜面があるかどうか、等を知るために使用されます。
- Max Penetration は、キャラクターが他の物理オブジェクトに侵入したときの動きを滑らかにします。キャラクターがMax Penetrationを通過すると、ハードフィックスが適用され、正しい位置にスナップされます。この値をゼロにすると、すべての修正が完全かつ瞬時に適用されます。これにより動きにが荒くなる可能性があります。
- Extent は、衝突が事前に検出される半径を定義します。
- Max Contacts は、KCCによって計算される連絡先の数を選択するために使用されます。1は通常は正常に機能し、最もパフォーマンスの高いオプションです。 動きがぎくしゃくした場合は、2に設定してみてください。 追加のオーバーヘッドは無視できる程度のものです。
- Layer Mask は、KCCが実行する物理クエリでどのコライダーレイヤーを考慮すべきかを定義します。
- Air Control を
Trueに切り替えると、KCCが地面に触れていないときに移動調整を実行できます。 - Acceleration は、キャラクターが加速する速度を定義します。
- Base Jump Impulse は、KCCの
Jump()メソッドを呼び出すときのインパルスの強さを定義します。 メソッドに値が渡されない場合、この値が使用されます。 - Max Speed は、キャラクターの最大水平速度を制限します。
- Gravity は、KCCに重力を適用します。
- Max Slope は、キャラクターが上下に歩くことができる最大角度を度数で定義します。
- Max Slope Speed は、移動タイプが水平落下ではなく傾斜落下の場合に、キャラクターが傾斜を滑り落ちる速度を制限します。
CharacterController API
以下に示すAPIは、3D KCCに焦点を当てています。2D APIと3D APIは非常に似ています。
プロパティとフィールド
各CharacterControllerコンポーネントにはこれらのフィールドがあります。
C#
public FP MaxSpeed { get; set;}
public FPVector3 Velocity { get; set;}
public bool Grounded { get; set;}
public FP CurrentSpeed { get;}
public AssetGUID ConfigId { get;}
ヒント
MaxSpeed は初期化後のキャッシュ値です。したがって、実行時に変更できます。例えば、ダッシュを実行するときです。
API
各KCCコンポーネントには、次の2つの方法があります。
C#
// Initialization
public void Init(CharacterController3DConfig config = null);
// Jump
public void Jump(FP? impulse, bool ignoreGrounded = false);
public void Jump(bool ignoreGrounded = false);
// Move
public static FPVector3 Move(void* entity, Transform3D* transform, CharacterController3D* kcc, FPVector3 direction, DynamicScene3D scene, FP deltaTime, IKCCCallbacks callback = null);
// Raw Information
public static CharacterController3DMovement ComputeRawMovement(void* entity, Transform3D* transform, CharacterController3D* kcc, FPVector3 velocity, DynamicScene3D scene, FP deltaTime, IKCCCallbacks callback = null);
Jumpと Moveメソッドはプロトタイプを作成するのに便利です。そして、ComputeRawMovementは独自の動きを作成するための重要な情報を提供します。Quantumが提供しているKCCの例では、ComputeRawMovementの情報は内部のステアリングメソッドComputeRawSteerで使用され、Moveで使用されるステアリングを計算します。
重要:
Jump()、Move()、ComputeRawSteer()の実装を以下に示しますが、これはゲームの要件に合わせたカスタム実装を作る際の参考にしてください。
CharacterController3DMovement
ComputeRawMovement()は、ShapeOverlapを実行してデータを処理することで、ステアリングに必要な環境データを計算する。このメソッドは CharacterController3DMovement 構造体を返し、これをキャラクターの動きに適用することができます。また、提供された動きのデータを使って、カスタムステアリングの実装を行うこともできます。
CharacterController3DMovement構造には次の情報が含まれます:
C#
public enum CharacterMovementType
{
None, // grounded with no desired direction passed
FreeFall, // no contacts within the Radius
SlopeFall, // there is at least 1 ground contact within the Radius, specifically a contact with a normal angle vs -gravity <= maxSlopeAngle). It is possible to be "grounded" without this type of contact (see Grounded property in the CharacterController3DMovement)
Horizontal, // there is NO ground contact, but there is at least one lateral contact (normal angle vs -gravity > maxSlopeAngle)
}
public struct CharacterController3DMovement
{
public CharacterMovementType Type;
// the surface normal of the closest unique contact
public FPVector3 NearestNormal;
// the average normal from all contacts
public FPVector3 AvgNormal;
// the normal of the closest contact that qualifies as ground
public FPVector3 GroundNormal;
// the surface tangent (from GroundNormal and the derived direction) for Horizontal move, or the normalized desired direction when in CharacterMovementType.FreeFall
public FPVector3 Tangent;
// surface tangent computed from closest the contact normal vs -gravity (does not consider current velocity of CC itself).
public FPVector3 SlopeTangent;
// accumulated projected correction from all contacts within the Radius. It compensates with dot-products to NOT overshoot.
public FPVector3 Correction;
// max penetration of the closest contact within the Radius
public FP Penetration;
// uses the EXTENDED radius to assign this Boolean AND the GroundedNormalas to avoid oscilations of the grounded state when moving over slightly irregular terrain
public Boolean Grounded;
// number of contacts within Radius
public int Contacts;
}
ComputeRawMovement()はMove()メソッドによって使用されます。
Jump
Jumpは単にKCCの現在の速度にインパルスを追加し、内部の ComputeRawSteer メソッドで処理される_Jumped_ブール値を切り替えます。
C#
public void Jump(FrameBase frame, bool ignoreGrounded = false, FP? impulse = null) {
if (Grounded || ignoreGrounded) {
if (impulse.HasValue)
Velocity.Y.RawValue = impulse.Value.RawValue;
else {
var config = frame.FindAsset(Config);
Velocity.Y.RawValue = config.BaseJumpImpulse.RawValue;
}
Jumped = true;
}
}
Move()
Move() は以下を考慮に入れながら文字の位置を返します。
- 現在の位置
- 方向
- 重力
- ジャンプ
- 斜面
- その他
これらすべての側面は、 Init()メソッドに渡される設定アセットで定義できます。これは、地形、メッシュコライダー、プリミティブを持つFPS/TPS/アクションゲームのプロトタイピングに便利です。
NOTE: すべてを計算し、最終的に FPVector3 の結果を返すので、動きそのものをあまりコントロールすることはできません。動きをより厳密に制御するには、ComputeRawMovement()を使用して、独自のステアリングと動きを作成する必要があります。
C#
public void Move(FrameBase frame, EntityRef entity, FPVector3 direction, IKCCCallbacks3D callback = null, int layerMask = -1, Transform3D* transform = null, Boolean? useManifoldNormal = null, FP? deltaTime = null) {
if (transform == null) {
Assert.Check(frame.Has<Transform3D>(entity));
transform = frame.Unsafe.GetPointer<Transform3D>(entity);
}
var dt = deltaTime ?? frame.DeltaTime;
CharacterController3DMovement movementPack;
fixed (CharacterController3D* thisKcc = &this) {
movementPack = ComputeRawMovement(frame, entity, transform, thisKcc, direction, callback, layerMask, useManifoldNormal);
}
ComputeRawSteer(frame, ref movementPack, dt);
var movement = Velocity * dt;
if (movementPack.Penetration > FP.EN3) {
var config = frame.FindAsset(Config);
if (movementPack.Penetration > config.MaxPenetration) {
movement += movementPack.Correction;
} else {
movement += movementPack.Correction * config.PenetrationCorrection;
}
}
transform->Position += movement;
}
ComputeRawSteer
ステアリングでは、キャラクターの位置、半径、速度から動きを計算し、必要に応じて動きを修正します。
ComputeRawSteerは内部メソッドで、キャラクターの現在の動作の種類に基づいて動作の計算の大部分を行います。KCCの例では、Moveは ComputeRawMovementから movementPackの値を要求し、それを ComputeRawSteer に渡します。
C#
internal void ComputeRawSteer(FrameBase f, ref CharacterController3DMovement movementPack, FP dt) {
Grounded = movementPack.Grounded;
var config = f.FindAsset(Config);
var minYSpeed = -FP._100;
var maxYSpeed = FP._100;
switch (movementPack.Type) {
// FreeFall
case CharacterMovementType.FreeFall:
Velocity.Y -= config._gravityStrength * dt;
if (!config.AirControl || movementPack.Tangent == default(FPVector3)) {
Velocity.X = FPMath.Lerp(Velocity.X, FP._0, dt * config.Braking);
Velocity.Z = FPMath.Lerp(Velocity.Z, FP._0, dt * config.Braking);
} else {
Velocity += movementPack.Tangent * config.Acceleration * dt;
}
break;
// Grounded movement
case CharacterMovementType.Horizontal:
// apply tangent velocity
Velocity += movementPack.Tangent * config.Acceleration * dt;
var tangentSpeed = FPVector3.Dot(Velocity, movementPack.Tangent);
// lerp current velocity to tangent
var tangentVel = tangentSpeed * movementPack.Tangent;
var lerp = config.Braking * dt;
Velocity.X = FPMath.Lerp(Velocity.X, tangentVel.X, lerp);
Velocity.Z = FPMath.Lerp(Velocity.Z, tangentVel.Z, lerp);
// we only lerp the vertical velocity if the character is not jumping in this exact frame,
// otherwise it will jump with a lower impulse
if (Jumped == false) {
Velocity.Y = FPMath.Lerp(Velocity.Y, tangentVel.Y, lerp);
}
// clamp tangent velocity with max speed
var tangentSpeedAbs = FPMath.Abs(tangentSpeed);
if (tangentSpeedAbs > MaxSpeed) {
Velocity -= FPMath.Sign(tangentSpeed) * movementPack.Tangent * (tangentSpeedAbs - MaxSpeed);
}
break;
// Sliding due to excessively steep slope
case CharacterMovementType.SlopeFall:
Velocity += movementPack.SlopeTangent * config.Acceleration * dt;
minYSpeed = -config.MaxSlopeSpeed;
break;
// No movement, only deceleration
case CharacterMovementType.None:
var lerpFactor = dt * config.Braking;
if (Velocity.X.RawValue != 0) {
Velocity.X = FPMath.Lerp(Velocity.X, default, lerpFactor);
if (FPMath.Abs(Velocity.X) < FP.EN1) {
Velocity.X.RawValue = 0;
}
}
if (Velocity.Z.RawValue != 0) {
Velocity.Z = FPMath.Lerp(Velocity.Z, default, lerpFactor);
if (FPMath.Abs(Velocity.Z) < FP.EN1) {
Velocity.Z.RawValue = 0;
}
}
// we only lerp the vertical velocity back to 0 if the character is not jumping in this exact frame,
// otherwise it will jump with a lower impulse
if (Velocity.Y.RawValue != 0 && Jumped == false) {
Velocity.Y = FPMath.Lerp(Velocity.Y, default, lerpFactor);
if (FPMath.Abs(Velocity.Y) < FP.EN1) {
Velocity.Y.RawValue = 0;
}
}
minYSpeed = 0;
break;
}
// horizontal is clamped elsewhere
if (movementPack.Type != CharacterMovementType.Horizontal) {
var h = Velocity.XZ;
if (h.SqrMagnitude > MaxSpeed * MaxSpeed) {
h = h.Normalized * MaxSpeed;
}
Velocity.X = h.X;
Velocity.Y = FPMath.Clamp(Velocity.Y, minYSpeed, maxYSpeed);
Velocity.Z = h.Y;
}
// reset jump state
Jumped = false;
}
衝突コールバック
KCCがコライダーとの交差を検出するたびに、コールバックがトリガーされます。
C#
public interface IKCCCallbacks2D
{
bool OnCharacterCollision2D(FrameBase f, EntityRef character, Physics2D.Hit hit);
void OnCharacterTrigger2D(FrameBase f, EntityRef character, Physics2D.Hit hit);
}
public interface IKCCCallbacks3D
{
bool OnCharacterCollision3D(FrameBase f, EntityRef character, Physics3D.Hit3D hit);
void OnCharacterTrigger3D(FrameBase f, EntityRef character, Physics3D.Hit3D hit);
}
コールバックを受け取り、その情報を使用するには、対応する IKCCCallbacksインターフェイスをシステムに実装します。
重要 衝突コールバックはブール値を返します。これにより、衝突を無視するかどうかを決定できます。falseを返すと、キャラクターは衝突した物理オブジェクトを通過します。
コールバックを実装する以外に、移動メソッドは IKCCCallbacksオブジェクトも渡す必要があります。以下は、衝突コールバックを使用したコードスニペットです。
C#
public unsafe class SampleSystem : SystemMainThread, IKCCCallbacks3D
{
public bool OnCharacterCollision3D(FrameBase f, EntityRef character, Physics3D.Hit3D hit) {
// read the collision information to decide if this should or not be ignored
return true;
}
public void OnCharacterTrigger3D(FrameBase f, EntityRef character, Physics3D.Hit3D hit) {
}
public override void Update(Frame f) {
// [...]
// adding the IKCCCallbacks3D as the last parameter (this system, in this case)
var movement = CharacterController3D.Move((Entity*)character, input->Direction, this);
// [...]
}